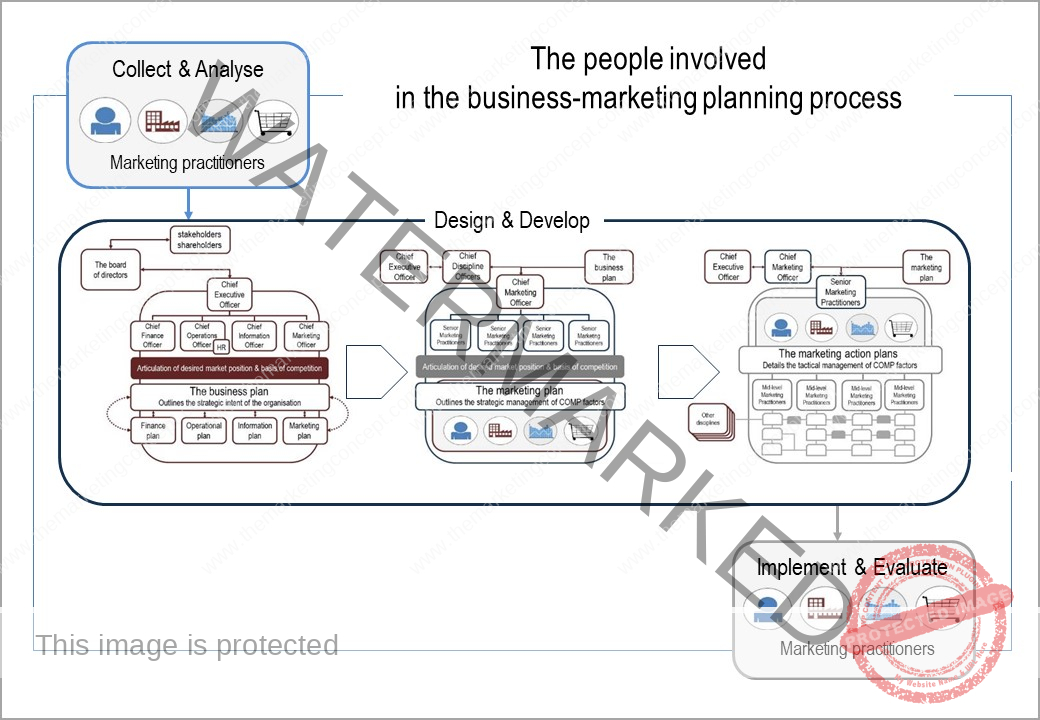
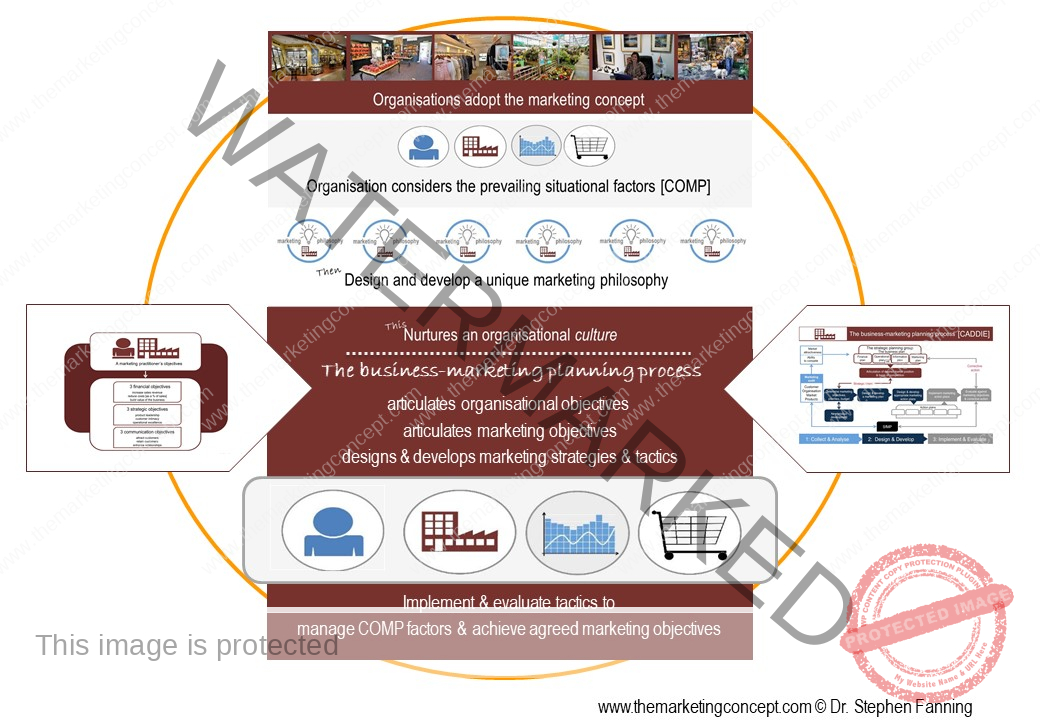
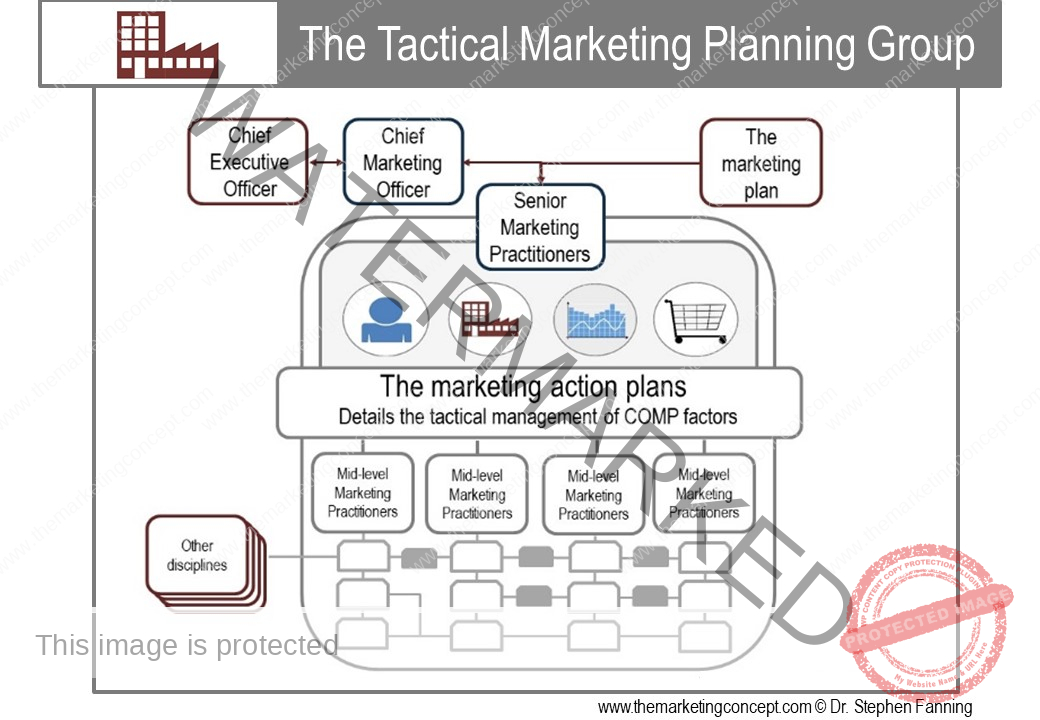
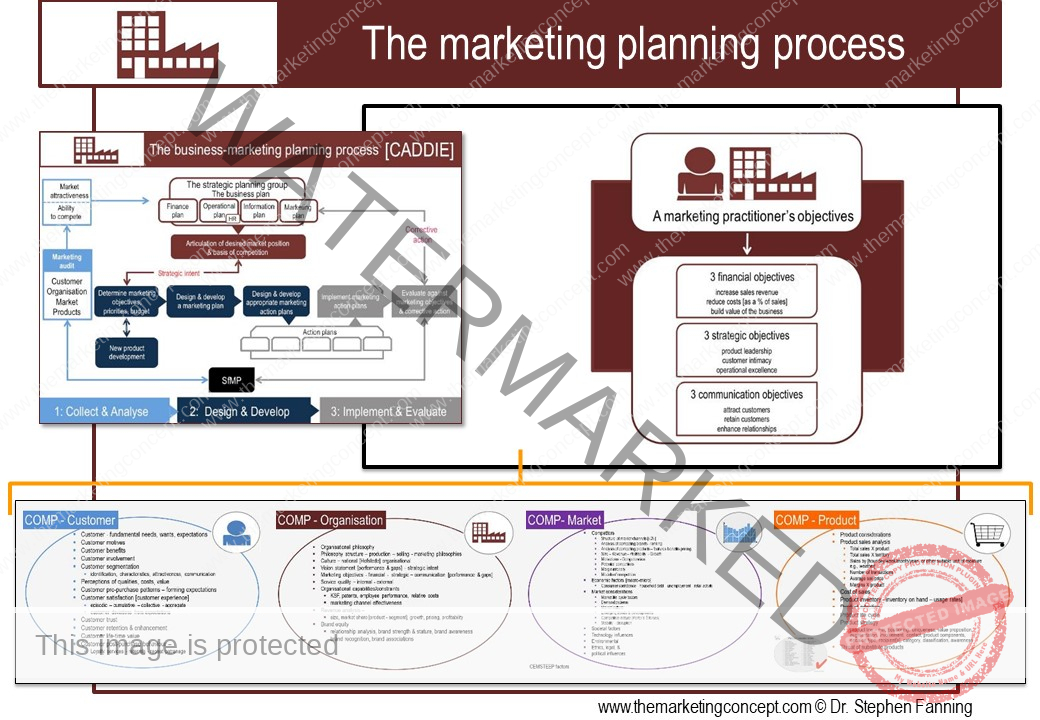
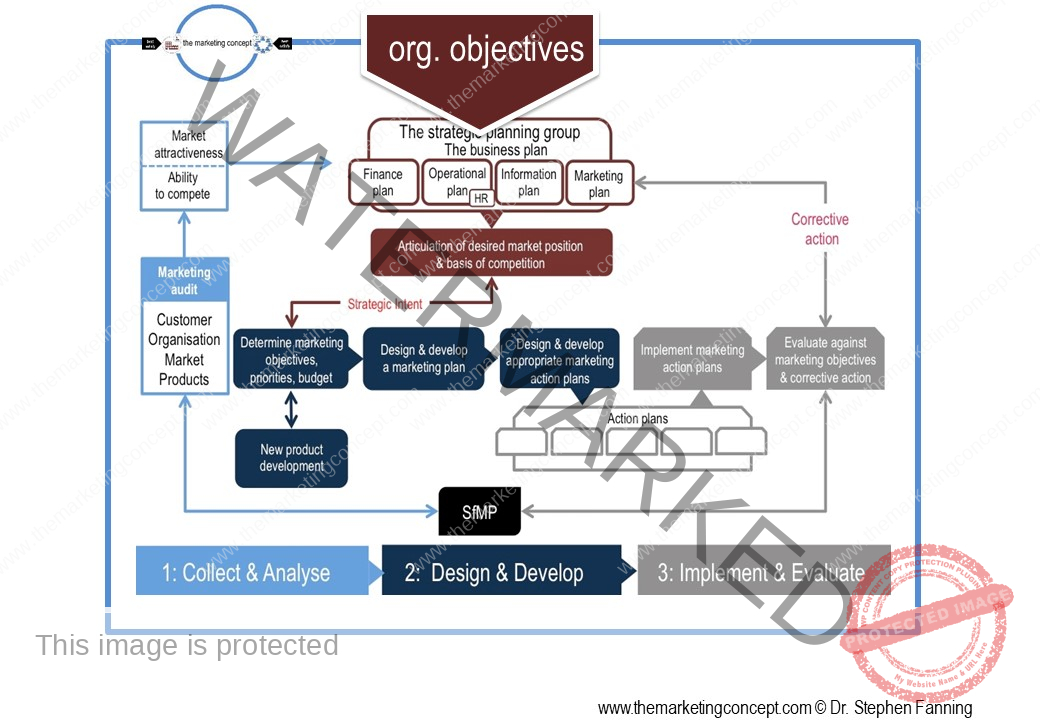
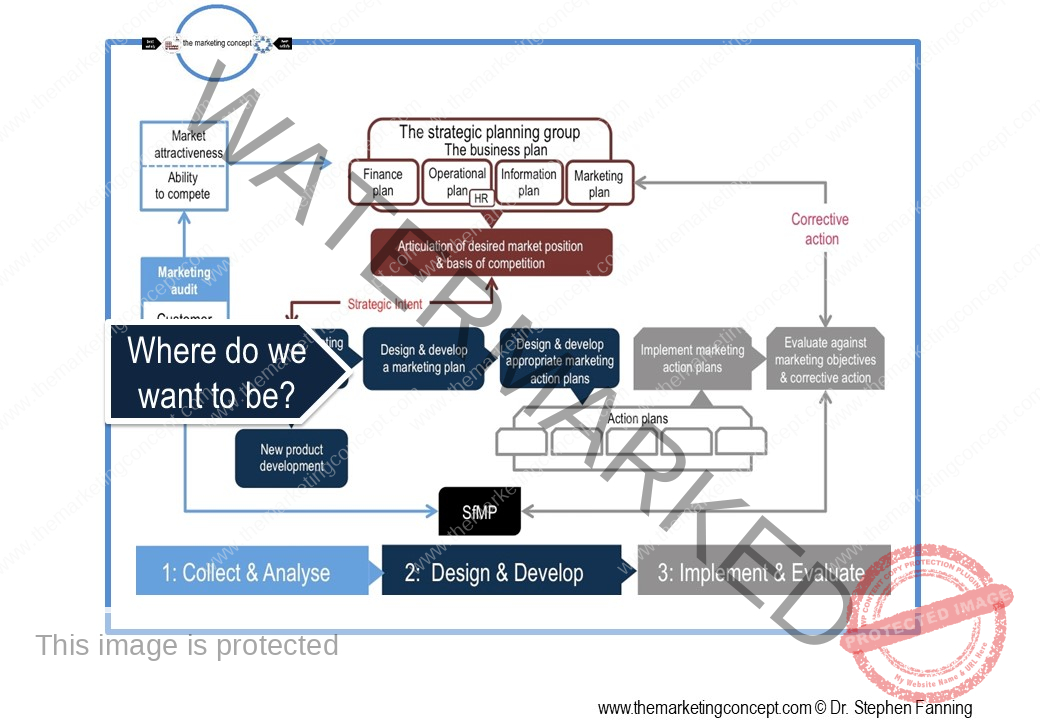
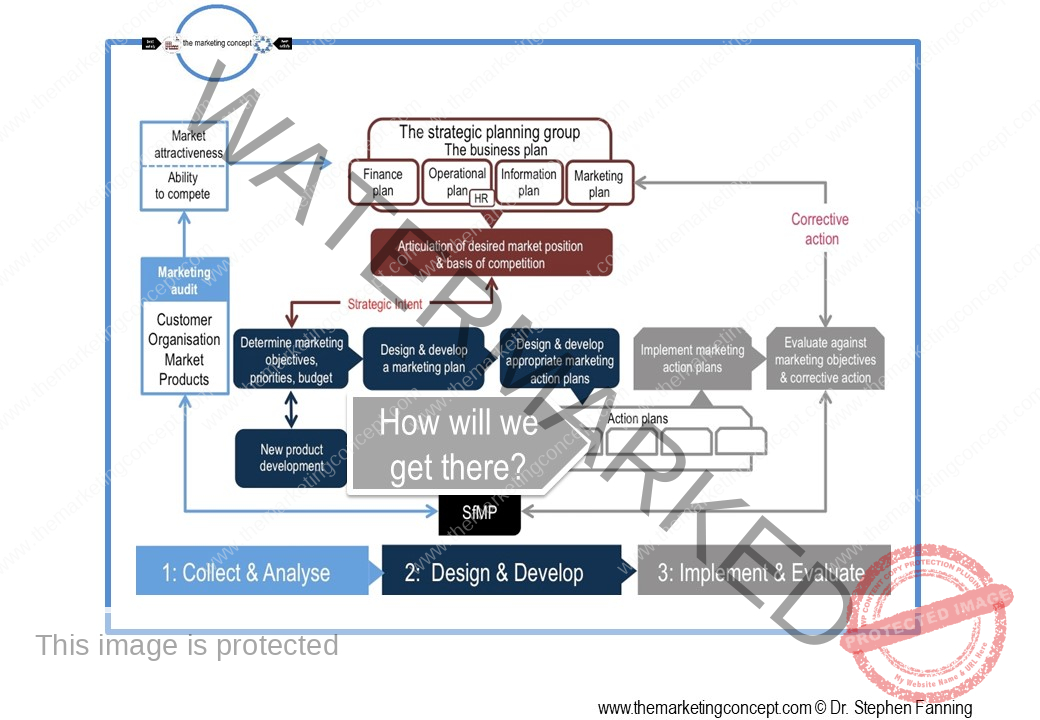
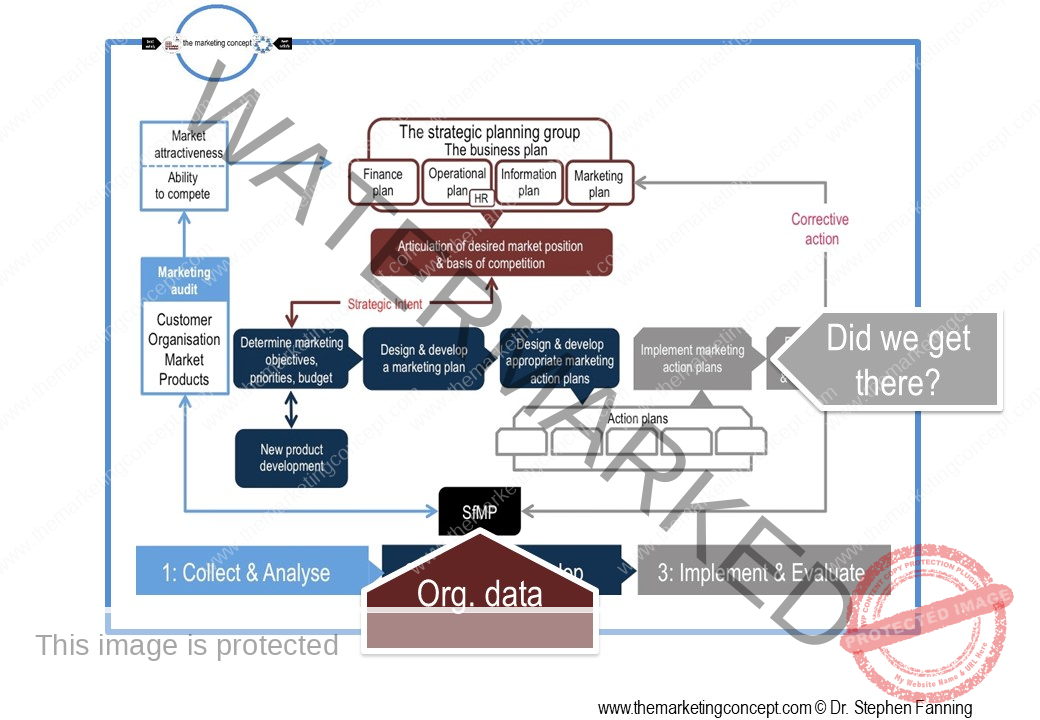
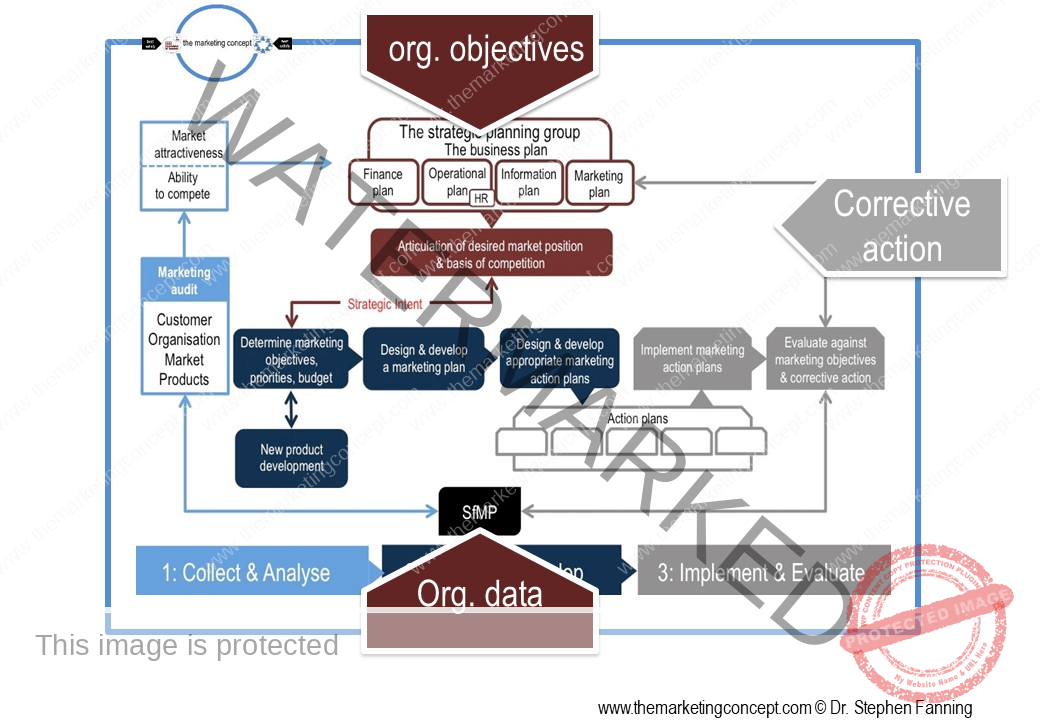
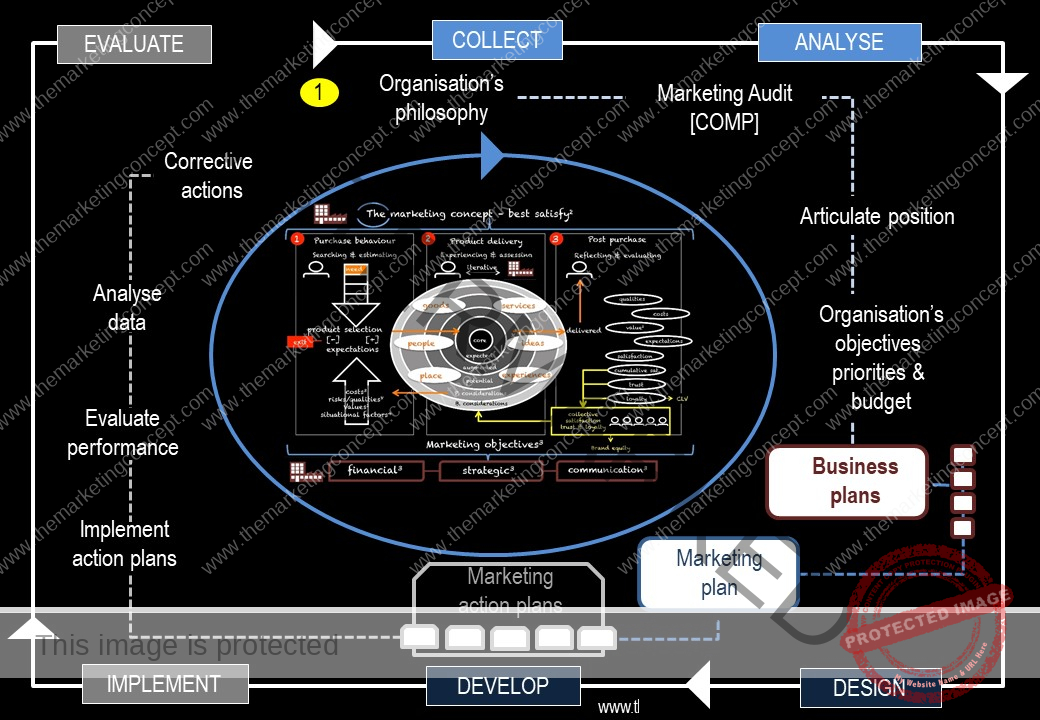
Learning objectives of the module: After completion of this module students should be able to demonstrate how the marketing concept and a marketing philosophy is transformed from strategic intent to tactical actions.
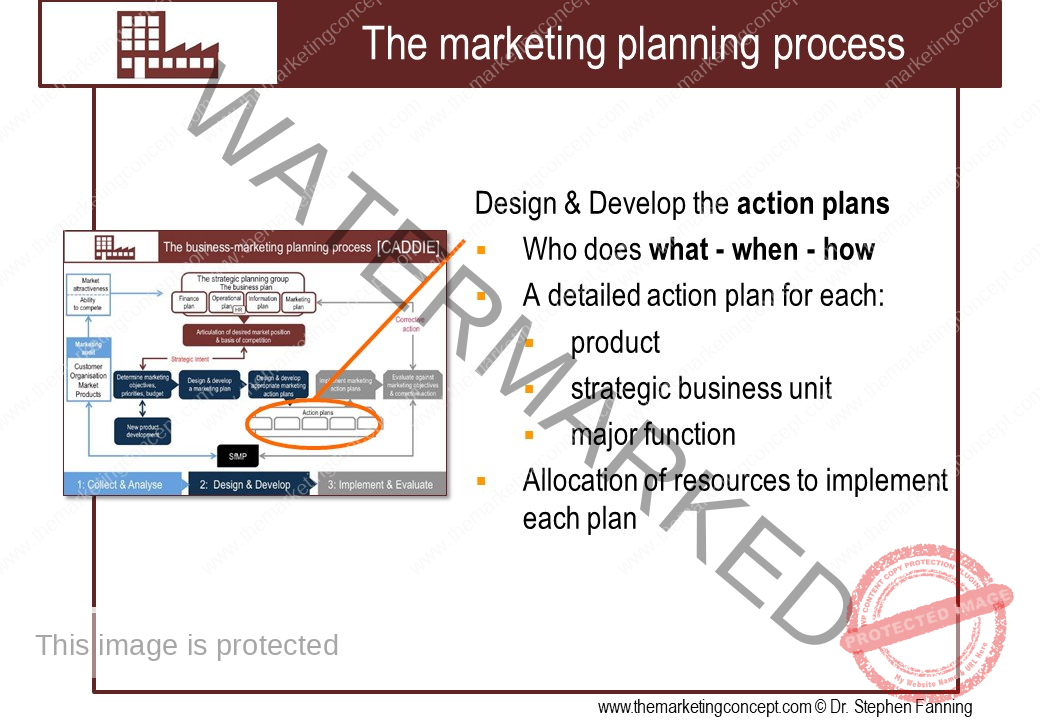
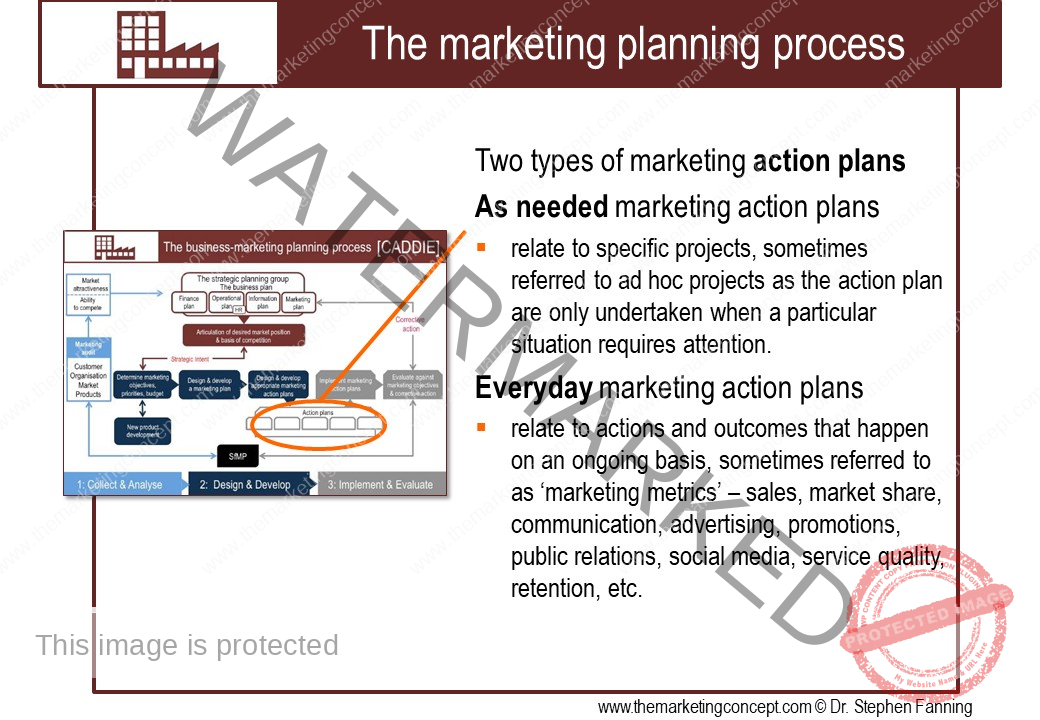
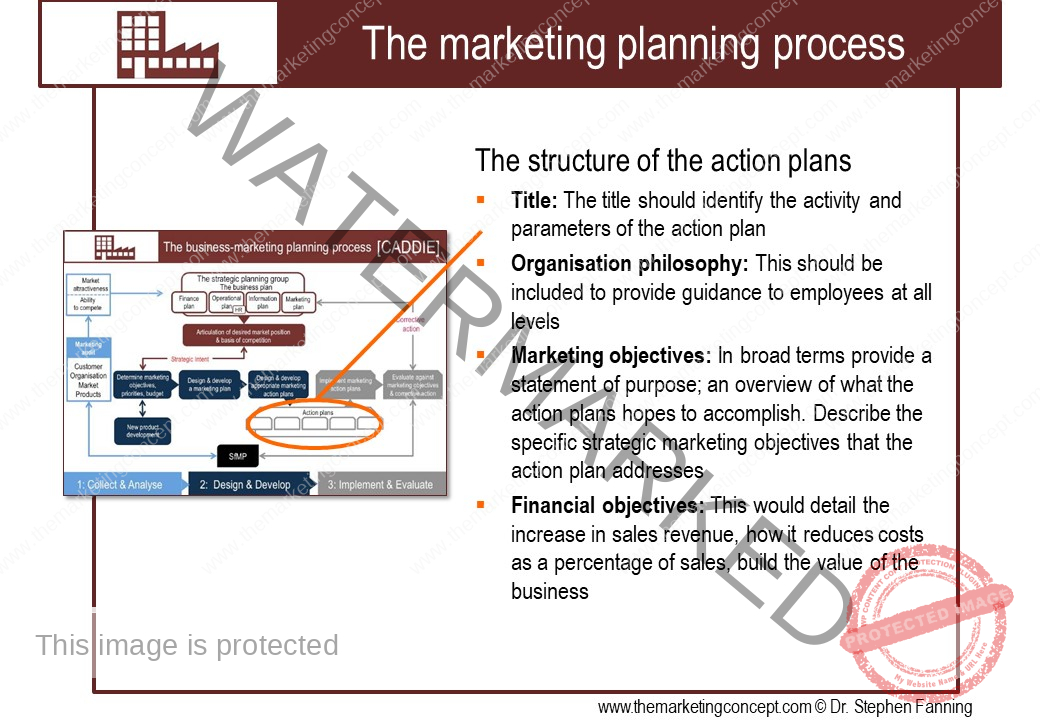
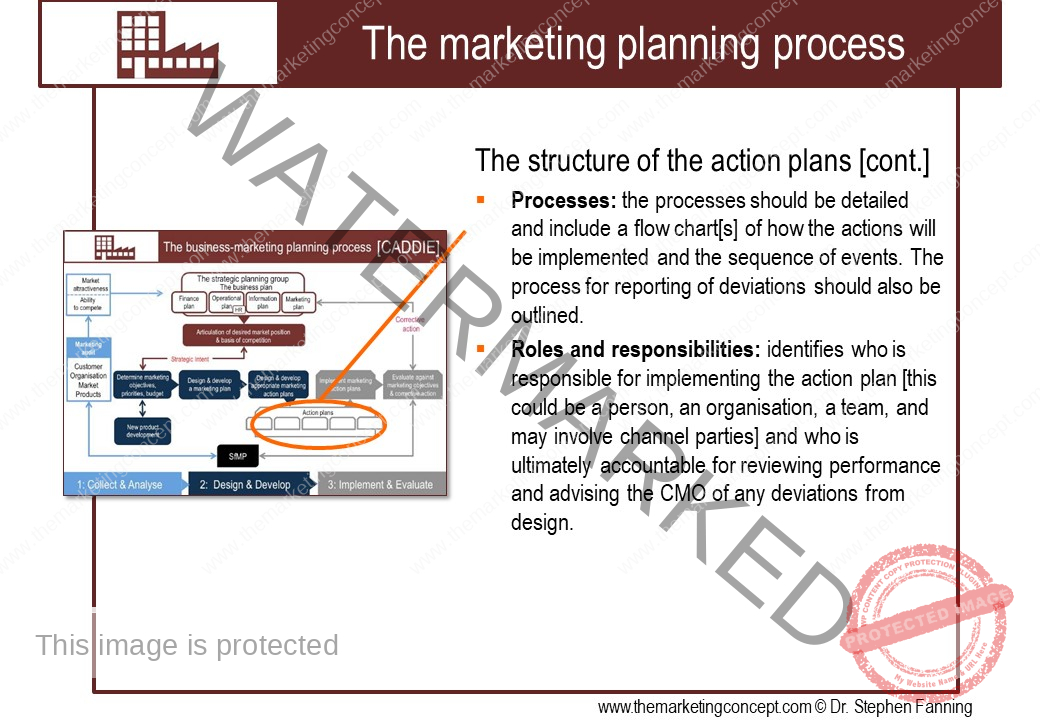
The module ‘The CADDIE process: implement & evaluate’ has a number of chapters. The chapters outline ‘typical’ marketing action plans of an organisation, however, this will vary from organisation to organisation and will include action plans that are ‘everyday’ and routine and ‘as needed’ due to changes in the situational factors the organisation expects to encounter. We explore the following marketing action plans:
- managing quality
- internal and channel marketing
- customer retention
- external marketing
- sales and salesforce management
- software for marketing practitioners
- the relational sales process
In this chapter of the marketing action plan module we discuss managing quality, We explore the 5-gap theory, the SERVQUAL tool, Net Promoter Score for measuring and managing customer satisfaction. In addition we synthesise our readings and suggest the quality can be technical quality, functional quality, relational quality and place quality.
In this chapter of the marketing action plans we explore why & how the objectives of profitable exchange relationships are communicated to internal customers and channel partners.
In this chapter of the marketing plan module we highlight th importance of managing customer retention and explain the organisational benefits of managing episodes of customer dissatisfaction.
In this chapter of the marketing action plan module we distinguish between internal and external marketing and discuss a broad understanding of the external marketing communication mix and how these applications can be applied to achieve the 9 objectives of marketing practitioners. Furthermore, we discuss a number of marketing concepts, including those that may provide guidance when managing controllable and uncontrollable elements.
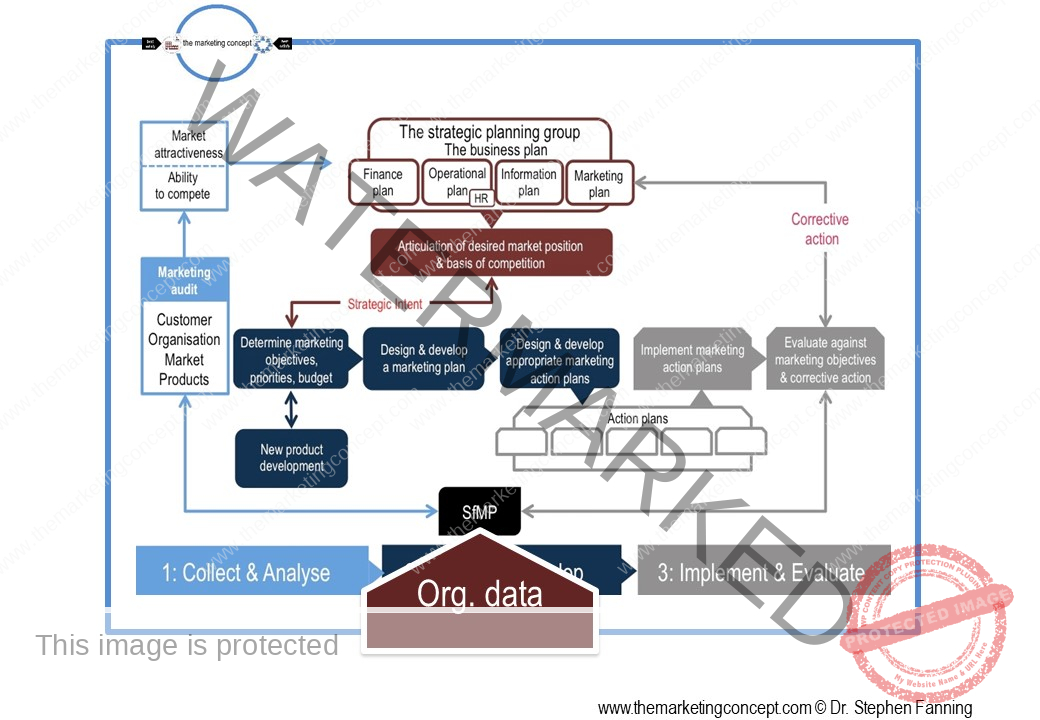
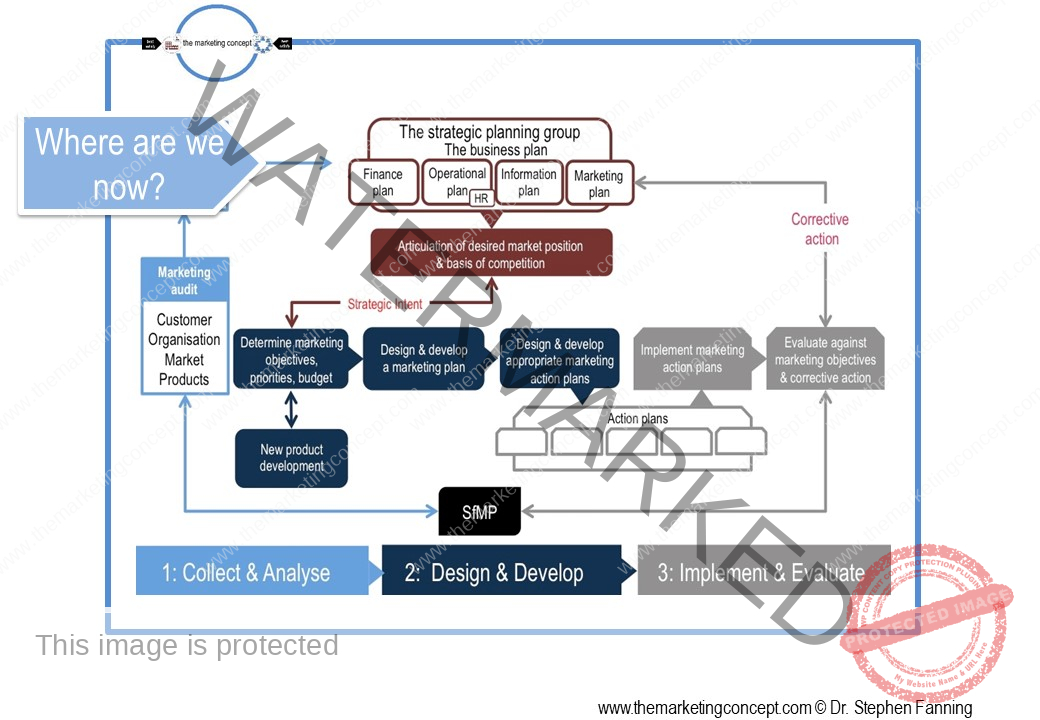
In this chapter of the marketing action plan module we discuss software for marketing practitioners [SfMP] and how it can assist marketing practitioners to make better more informed decisions throughout the CADDIE process. Moreover, we note that software for marketing practitioners may have a strategic or tactical focus.
In the chapter of the marketing action plans module we discuss sales leads as an asset that should be valued and managed, We then discuss the salespipeline and the steps in managing sales leads.